Guides
CardSavr Architecture
Strivve’s CardSavr Service is a Platform As A Service (PaaS) which securely places payment cards on merchant sites on behalf of; and with explicit authorization of; Card Issuers and their cardholders. It uses Remote Process Automation to perform this task. CardSavr is PCI-DSS 3.1 compliant.
Simplified View of the CardSavr Service Architecture
CarSavr systems architecture utilizes a modern Cloud architecture. It is implemented on the PCI-DSS compliant Amazon Web Services (AWS) public cloud and relies on underlying AWS services for portions of its overall security. It provides multi-tenancy infrastructure to meet the needs of Financial Institution isolation. At a minimum this isolation is provided by AWS Virtual Private Clouds (VPC) and depending upon the isolation requirements of a Financial Institution; within dedicated AWS sub accounts. Every PCI-DSS Cardholder Data Environment (CDE) is encapsulated within a VPC. A Financial Institution can optionally have multiple CDE’s and often do in order to segment their application development from their production environment. The following diagram illustrates a simplified view of a VPC/CDE.
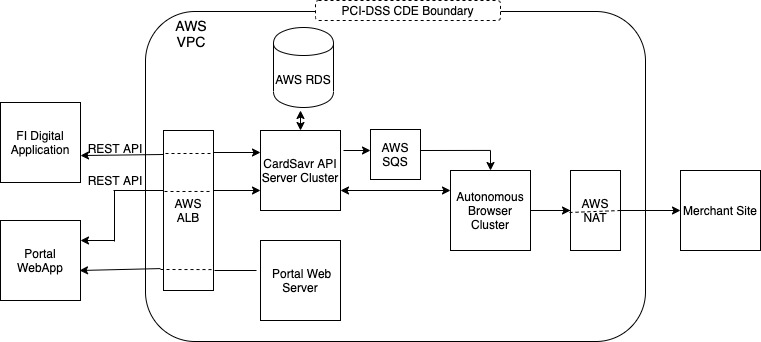
In this illustration, the CDE boundary is defined by the VPC. Every CDE is replicated across multiple AWS availability zones in a AWS Region, including multiple instances of each component in order to provide high availability and scalability. Each CDE has its own exclusive AWS RDS database to store Personal Identifiable Information (PII), Cardholder Data (CHD), Sensitive Authentication Data (SAD) and Merchant Credentials (MC), All Strivve developed components are single purpose servers encapsulated in hardened Docker containers and run as a cluster of tasks under the AWS Fargate orchestration management service on AWS EC2 virtual machines.
All CDEs run under the CardSavr top level domain cardsavr.io. Each CDE has its own subdomain environment name. CardSavr API is accessed as the subdomain api in the invidual CDE subdomain. Example api url takes the form: https://api.<*cde-environment-name*>.cardsavr.io/*endpoint*.
CardSavr API Server
CardSavr API Server is the central coordinator of the whole service. All temporary and persistent data is managed by this server and stored in a AWS RDS database. All card placement jobs are dispatched and managed by this server as well.
Autonomous Browser
CardSavrAutonomous Browser interacts with merchant sites acting as a Remote Process Automation agent to place payment cards on behalf of cardholders on their merchant accounts. It processes job requests dispatched to it via AWS SQS queues.
Portal Web Server & WebApp
CardSavr Portal Web Server hosts the Portal WebApp that is used by the Financial Institution as an administration tool for their CDE. The Portal WebApp interacts with the CardSavr Server using the CardSavr RESTful API.
Financial Institution Applications
Financial Institution applications interact with the CardSavr Server using the CardSavr RESTful API. Optional Software Developmemt Kits are available for select programming lanuguages to simplify integration with the RESTful API.
Application Integration with CardSavr
CardSavr provides a RESTful API at the protocol level. Like other RESTful API’s it utilizes HTTPS as the base construct protocol and layers in the API with a combination of HTTP headers and JSON bodies. This API has a number of endpoints, each with its own URL path and supports the standard REST Create Read Update Delete (CRUD) paradigm in which the following HTTP methods are utilized:
- Create is implemented with the POST method
- Read is implemented with the GET method
- Update is implemented with the PUT method
- Delete is implemented with the DELETE method
Given the sensitive nature of PCI CHD/SAD data and the cardholder’s merchant credentials; CardSavr implements a number of security mechanisms not typically found with RESTful APIs and can be more difficult to implement than many developers are used to. A Software Development Kit (SDK) is available for select programming languages which takes care of this complexity and enables the application developer to simplify interaction with the RESTful methods and JSON bodies of each endpoint. The following diagram illustrates the two API integration paths.
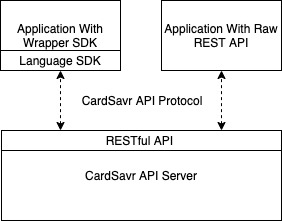
These security mechanisms include digital signing of all requests and responses, encryption of all request and response bodies, nonce replay attack prevention and ephemeral elliptic curve key exchange. Applications that integrate directly with this API must implement these capabilities. Applications that integrate using a language specific SDK do not have to implement these security mechanisms as they are performed by the SDK itself.
To learn more about low level security mechanisms of the platform, please contact E-mail Strivve for access to the Strivve Technical Security Overview.

